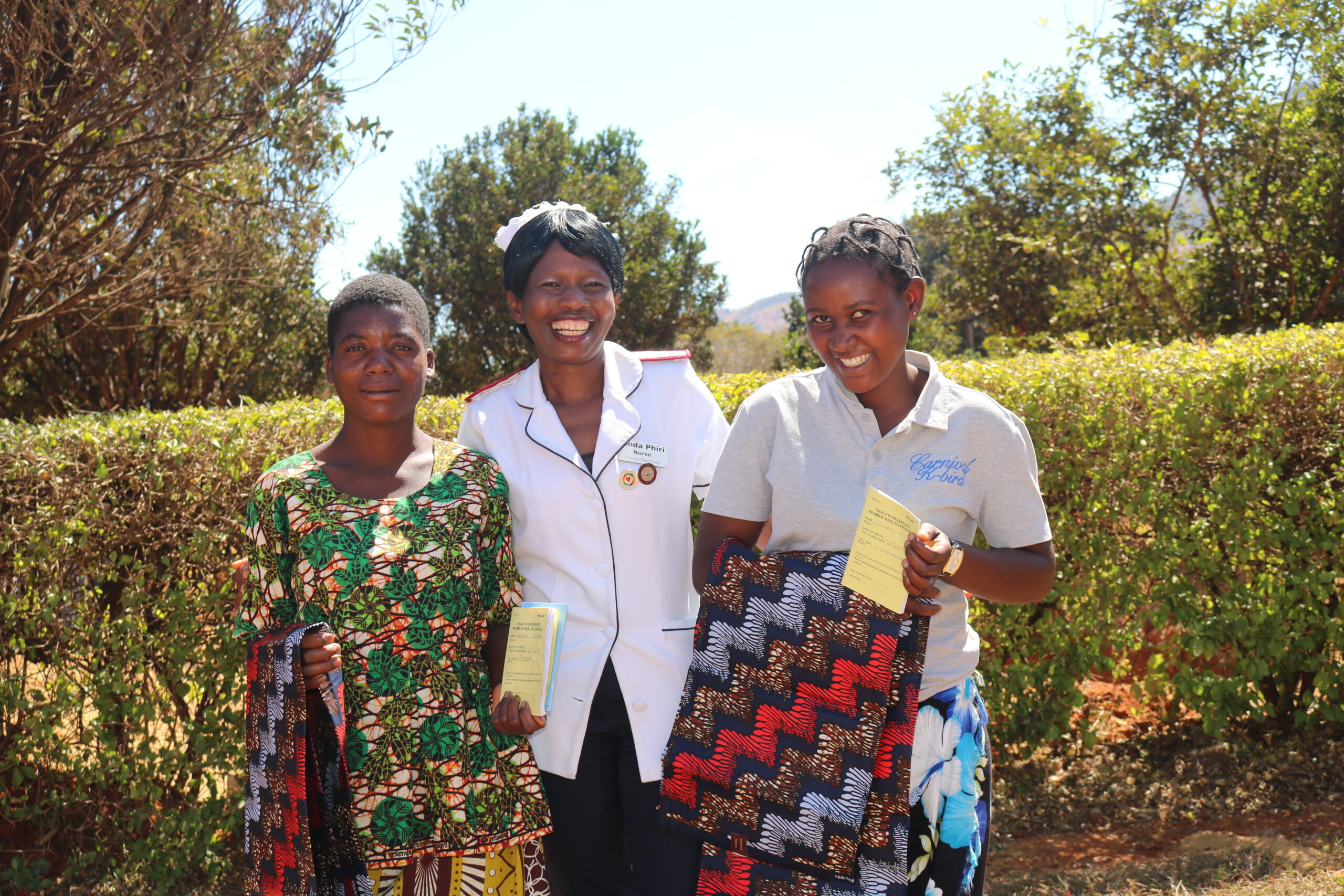
Last week, we were visited by the quality of care assessment team from Dowa District hospital. Read today's blog post to learn about how this exercise is important to us and the community we serve.
Getting Tested for Cervical Cancer in Malawi
why it matters and what to expect

Malawi has the highest cervical cancer incidence and mortality rate in the world, BMC Public Health reported in 2015. This means more women get cervical cancer in Malawi than anywhere else in the world. And more women in Malawi die from it, too. One of the main challenges in Malawi is late diagnosis. Late diagnosis is often caused by lack of information about testing. As a trusted healthcare provider in rural Malawi, Orant is here to answer all the questions you might have.
What is cervical cancer?
Cancer happens when cells begin to grow out of control. Cervical cancer starts in the lower part of the womb that connects to the birth canal. It is most common in women 30 years of age and older. If found early, it’s highly treatable. In its early stages, cervical cancer doesn’t have many symptoms. This is why screening is so important. If not treated, the cancer can spread out of the cervix and affect other tissues and organs.
Who should get tested?
All women who are sexually active. At Orant, we screen HIV positive people every year; HIV negative people every three years.
What does screening look like?
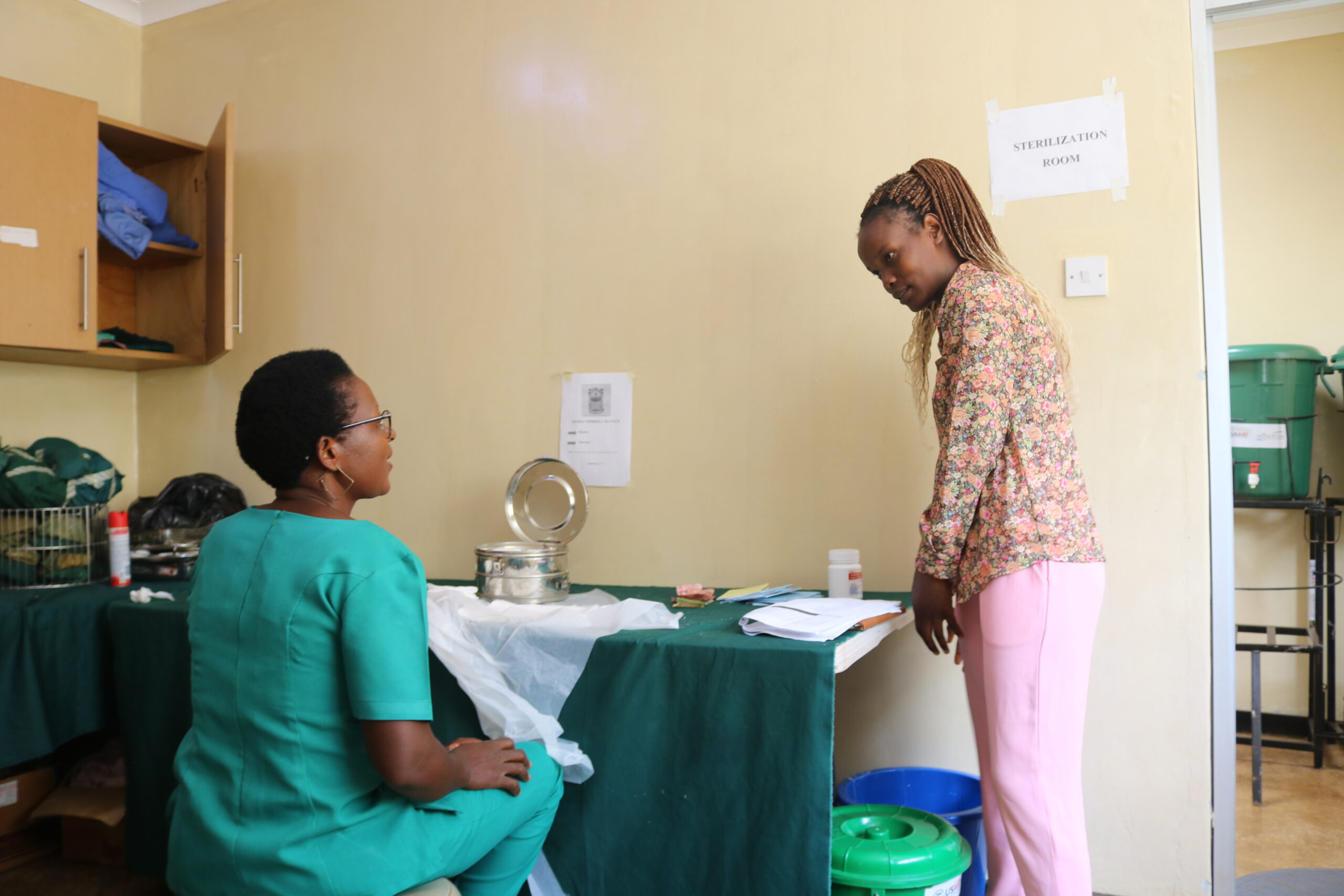
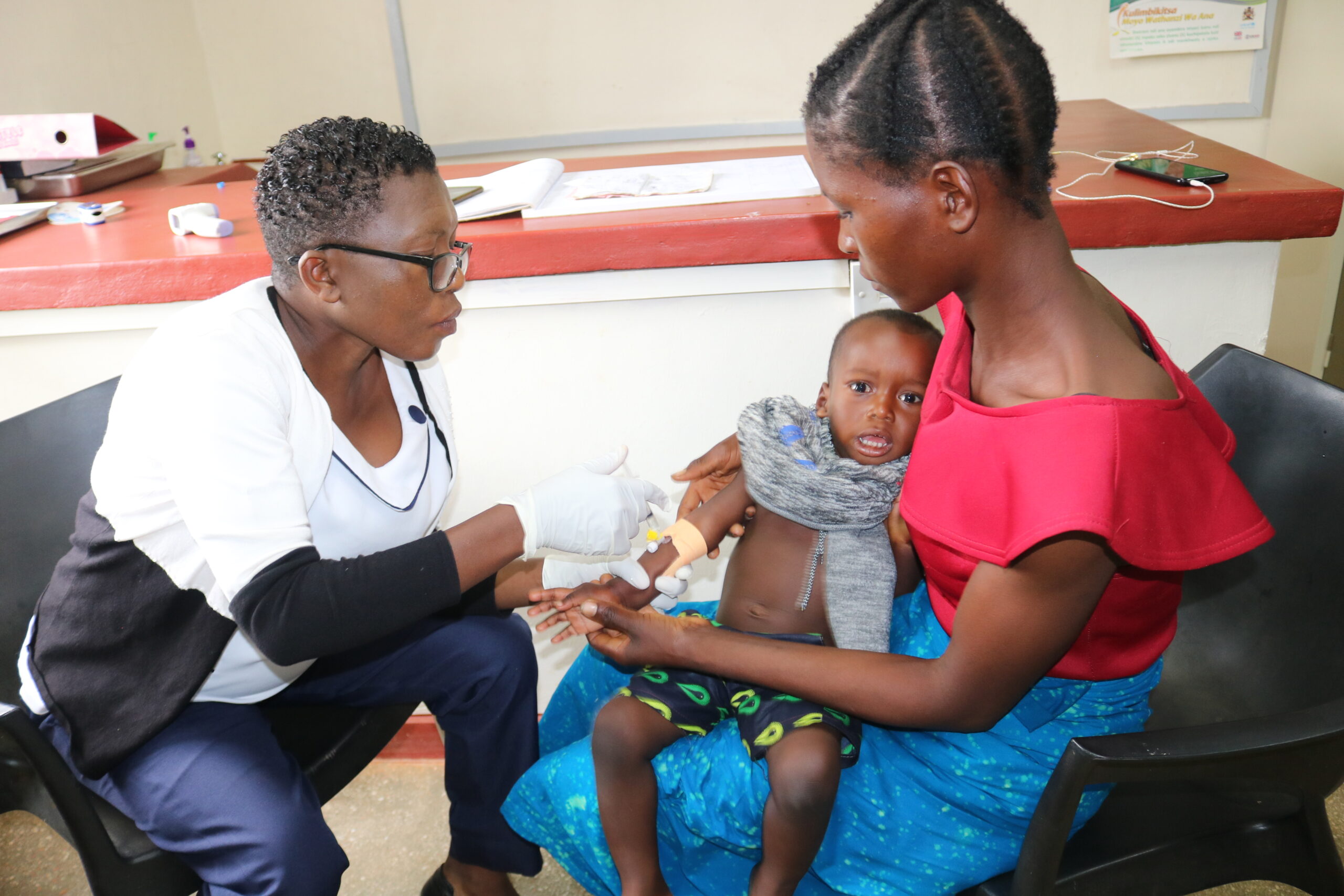
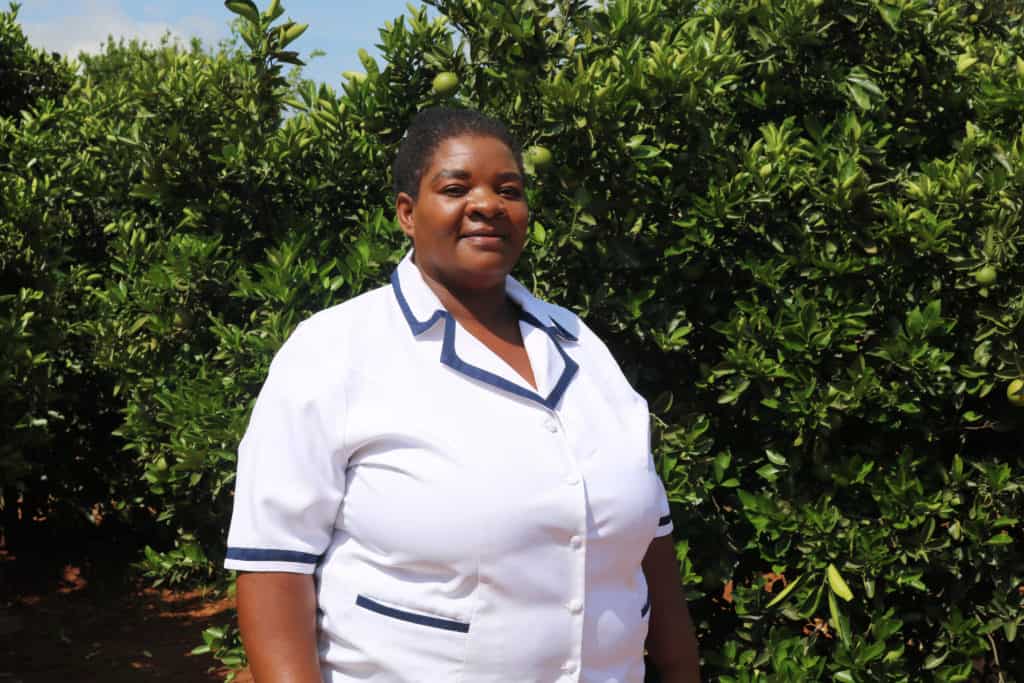
Orant’s Kasese Health Center provides screenings every Friday. Like many healthcare providers in Malawi, Orant uses VIA screening. VIA stands for Visual Inspection with Acetic Acid. The process is simple and painless. Orant nurse Mary Kadzola is carefully trained to identify VIA results. The patient’s cervix is swabbed with 3% to 5% acetic acid solution, which is essentially just table vinegar. To ensure the patient’s comfortability, Mary explains each step of the process. The screening takes place in a completely private room.
How much does testing in Malawi cost?
Testing at Orant’s Health Clinic is free. Testing is also free at all government hospitals and clinics. Private hospitals and clinics charge anywhere from 500 MWK to 2000 MWK.
What helps prevent cervical cancer?
- Regular screenings at a healthcare facility with trained professionals
- Limiting exposure to HPV by:
- Limiting number of sexual partners
- Practicing safe sex with condoms
- Avoiding sex with people who’ve had many sexual partners
- Avoiding sex with people infected with genital warts or other abnormalities
- Not smoking
How is cervical cancer treated in Malawi?
Orant treats cervical cancer with thermal coagulation. This treatment uses a small device to destroy lesions with heat.
We also refer anyone with lesions on their cervix to Kamuzu Central Hospital. We give these patients money for transportation, biopsy, monitoring, and assessment for up to 3 years. At the hospital, they receive further screening and biopsy.
Taking control of your body’s health is a sign of strength and self-compassion.
Get tested. Tell your friends, mothers, and sisters to get tested. Take care of yourself and each other. Cervical cancer is treatable.
Read about patient Glyceria Selemani’s strength and self-compassion here.
The Orant Journal
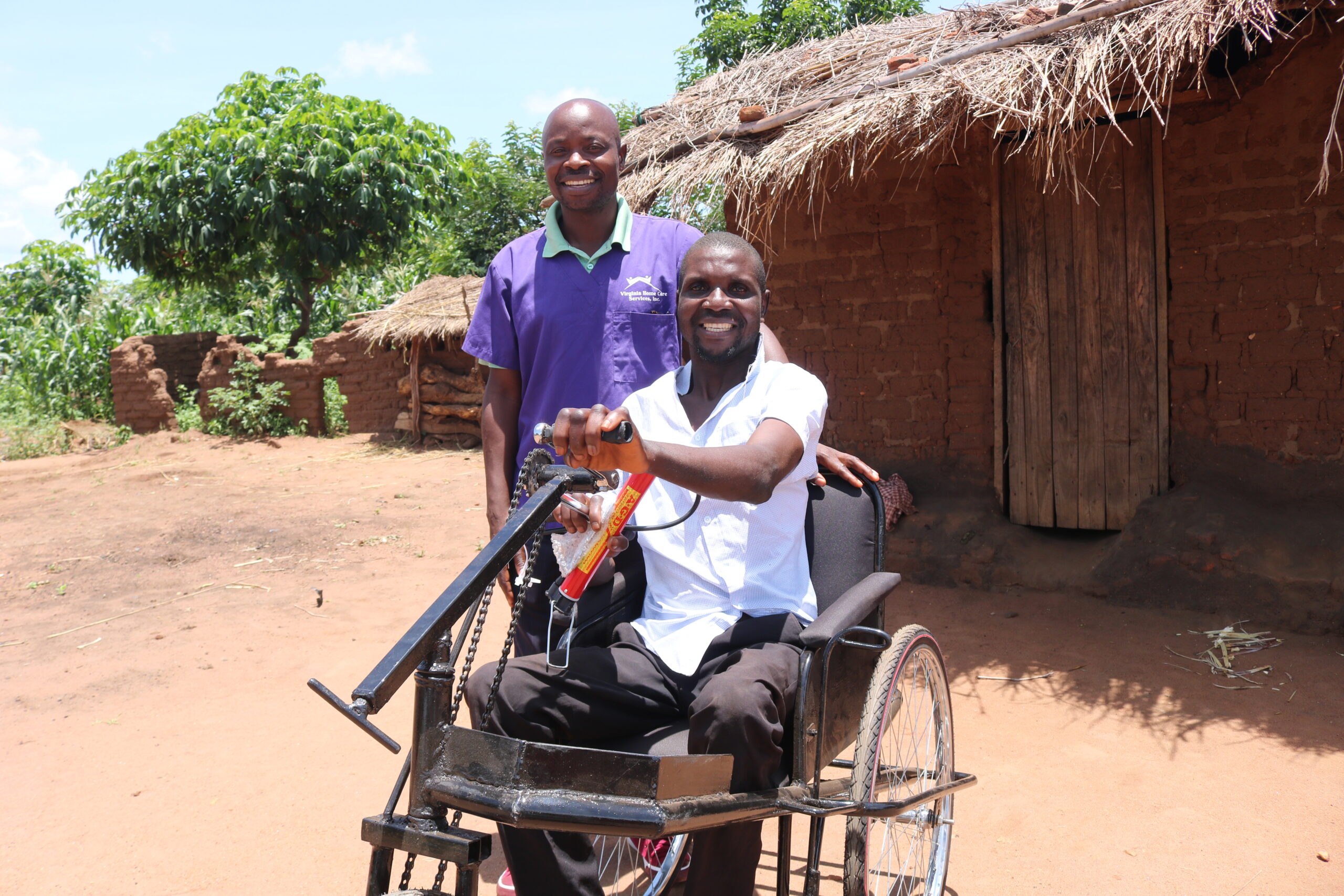
New Wheels from Orant’s Healthcare Program
We are always happy when our support brings a smile on peoples faces and changes their lives. In this week’s blog article, we are talking to Andrea Mwale, a 41 year old man from Chapuwala village in Kasese. Andrea shares his gratitude towards the support that our Healthcare program has recently provided to him.
School Surveys Lead to Better Learning Outcomes
Data is one of the most important tools in all our programs as it helps us measure whether our programs are making an impact or when it’s time for change. For the past three weeks, our Education program has been surveying schools in our catchment area. Check out today’s blog to learn more about how this survey is going to contribute to our Education program.
Improving Healthcare Access in Rural Malawi
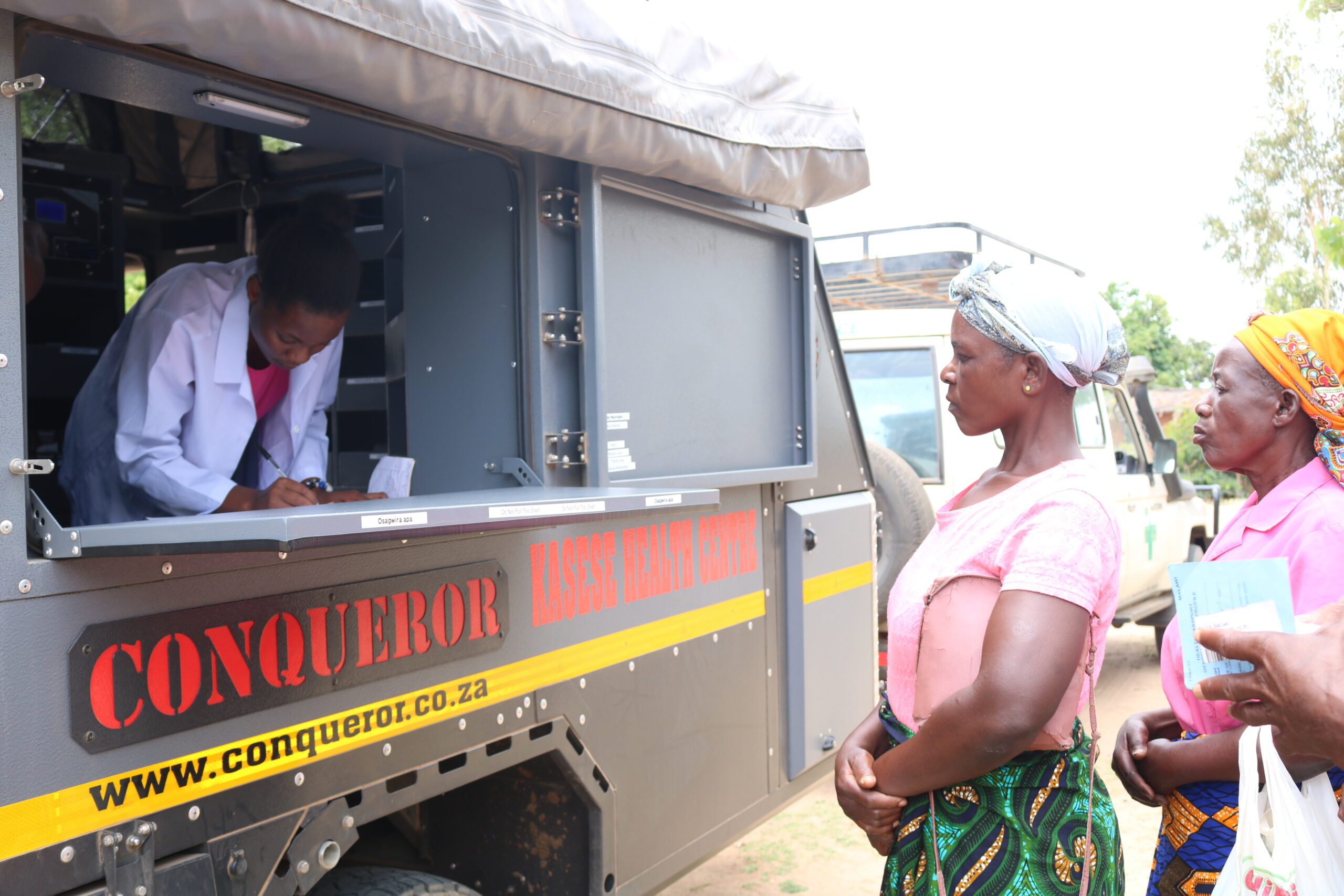
We are thrilled to announce the opening of our new Mobile Outreach Clinic this week, which is a great stride that our Healthcare program has achieved! We have started our operations with treating Chatalala Community in Kasungu district, Traditional Authority Njombwa. Read our blog post to learn more about how the new mobile outreach clinic will serve communities better.
Malaria Season in Malawi
Summer in the Southern Hemisphere brings malaria season in Malawi, a dangerous disease that can kill those who do not receive treatment in time. Orant works to ensure that those afflicted with the disease receive the proper treatment and recover.
The Challenge of Noncommunicable Diseases in Rural Malawi
Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) remain a huge burden to the healthcare sector in Malawi. Read our blog post to learn more about NCDs.
Conducting Mobile Outreach Clinics in Malawi
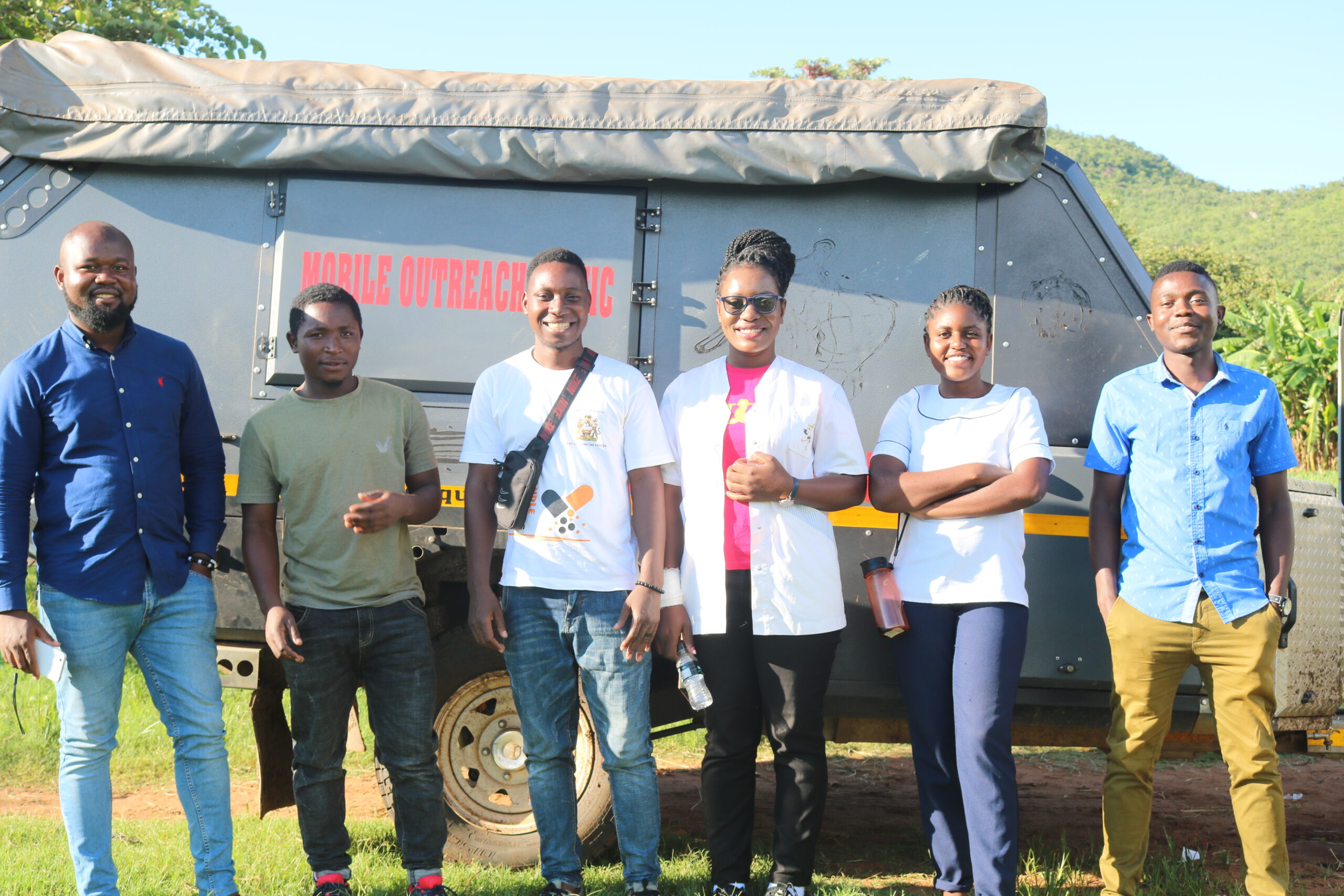
Your donations have purchased a new trailer for our Mobile Outreach Clinic! Read our latest blog as our Mobile Outreach Clinic (MOC) team shares how the new trailer will be of great help to the team’s daily operations.
A New Hope for Mothers in Malawi
In rural Malawi, pregnant women face many challenges including lack of access to prenatal care, poor nutrition, and lack of safe spaces to deliver their babies. Orant is working to change that with the renovation of our maternity ward. Read about it in this week’s blog.
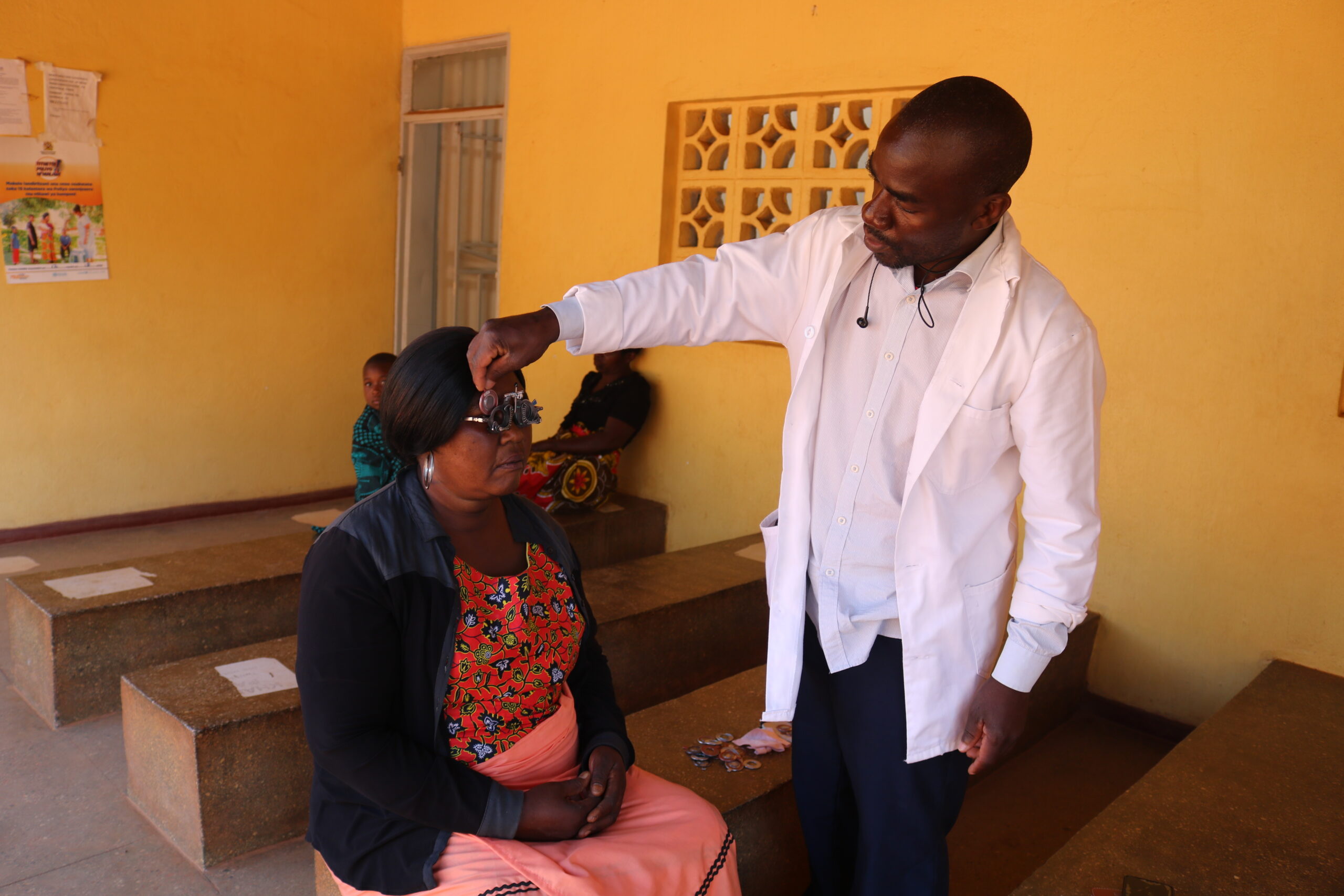
Orant Improves Eye Health in Rural Malawi
On the last Wednesday of every month, our Kasese Health Centre conducts eye clinics for local residents in need of treatment. Read our latest blog to learn more about our eye clinics and how they help people in rural Malawi.
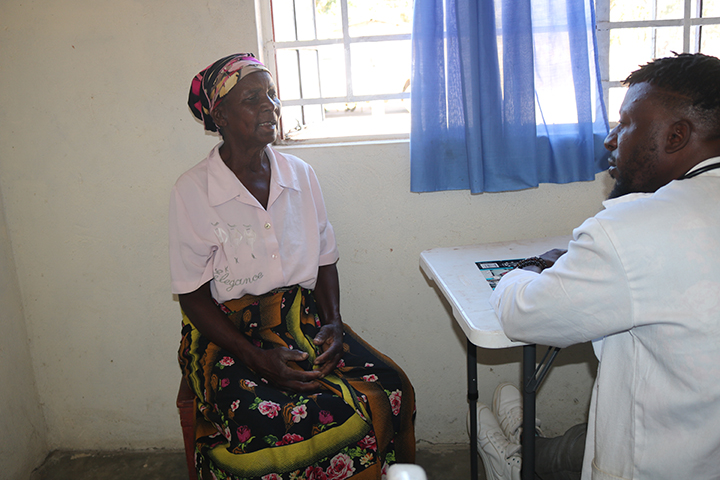
One of the greatest challenges that our Healthcare program faces is women starting antenatal care too late in their pregnancy. This puts the lives of pregnant mothers and their unborn babies at risk. Read our latest blog to learn about what our Healthcare program is doing to motivate pregnant mothers to start attending antenatal care as soon as they find out that they are pregnant.